团队负责人姜晓燕老师的论文“Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion with spatial-temporal geometric constraints”在IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME) 中被接收,祝贺!
Abstract:
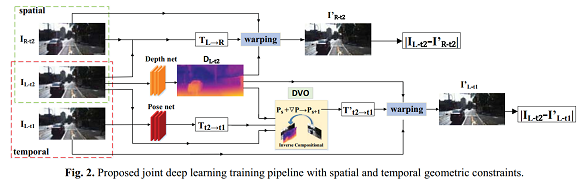
In this paper, we propose an unsupervised joint deep learning pipeline for depth and ego-motion estimation that explicitly incorporated with traditional spatial-temporal geometric constraints. The stereo reconstruction error provides the spatial geometric constraint to estimate the absolute scale depth. Meanwhile, the depth map with absolute scale and a pre-trained pose network serve as a good starting point for direct visual odometry (DVO), resulting in a fine-grained ego-motion estimation with the additional back-propagation signals provided to the depth estimation network. The proposed joint training pipeline enables an iterative coupling optimization process for accurate depth and precise ego-motion estimation. The experimental results show the state-of-the-art performance for monocular depth and ego-motion estimation on the KITTI dataset and a great generalization ability of the proposed approach.
Download: [官方链接]
Keywords: Depth, ego-motion, geometric constraint, visual odometry
Photos: